Sacroiliac Joint Hypermobility
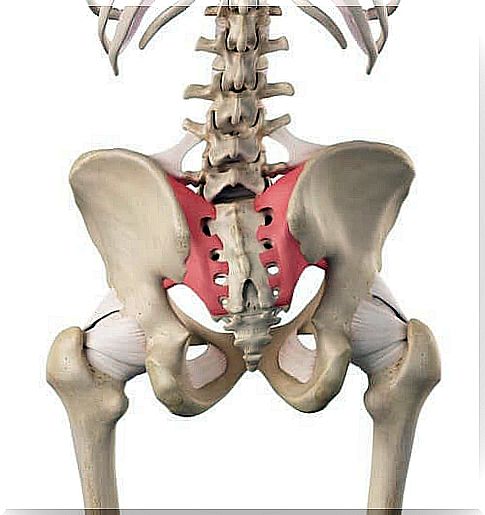
The sacroiliac joint is on the side of the lower spine, below the lower back, in the coccyx. It is a structure that connects the sacrum bone (triangular bone at the bottom of the spine) with the pelvis (iliac crest).
Both sacroiliac joint hypermobility and other conditions that affect this joint are generally more frequent in young and middle-aged women.
The sacroiliac joint has the following characteristics:
- It is small but very strong. It is reinforced by ligaments.
- It doesn’t have much mobility.
- It transmits all the forces from the upper body to the hips and legs.
- Acts as a shock absorber.
Anatomy of the sacroiliac joint
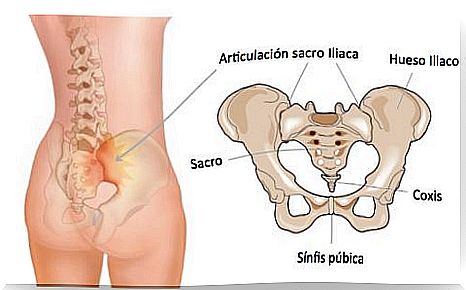
The pelvic girdle forms the base of the torso. In addition, it is also the support of the abdomen and makes a union between the lower limbs and the trunk. It is a closed osteoarticular ring composed of three bone pieces and three joints.
The three bone pieces are:
- 2 iliac bones, pairs and symmetrical.
- The sacred, odd and symmetrical.
- Vertebral block formed by the fusion of 5 sacral vertebrae.
The pelvis is of great importance in the unstable balance of the spine, as any change in the former will inevitably affect the latter. Therefore, we could consider it a functional unit.
The sacroiliac joints are the junction between the spinal column, which is flexible, above, and the stability of the pelvis, below. In addition, the sacrum is considered to be part of the lumbar vertebrae and the iliac part of the lower limbs.
Causes of pain in the sacroiliac joint
It is believed that an alteration in normal joint movement may be responsible for sacroiliac pain, however, it is currently unclear why pain occurs in this area.
The source of pain can be caused by:
- Sacroiliac hypermobility : ie when there is a lot of movement and instability in this area of the back. Pain is usually felt in the lower part or hip. It can also radiate to the groin area.
- Sacroiliac hypomobility : on the contrary, this situation occurs when there is very little movement or fixation in this area. Pain is usually felt in the lower back or buttocks. In this case, the pain may radiate through the leg.
Patients describe the pain as if it were similar to sciatica. It is caused by radiculopathy.
Sacroiliac joint assessment
There are numerous tests to examine the mobility of this joint and diagnose hypermobility or other conditions. Tests can be of different complexity and are usually tailored differently by each physiotherapist.
Furthermore, in the same test, different situations can be seen. Incidentally, it should be noted that the need for an anamnesis (a set of information) before these tests is also important, as it helps to guide the professional in this type of examination.
Some of these tests that are usually performed for diagnosis are:
- Sacroiliac joint mobility test : despite being quite general, the initial test should be considered to assess this joint, as it will provide the professional with information about the mobility in the structure.
- Downing Test : serves to determine the different injuries and establish the difference between the deficit in total or partial mobility of the iliac bones over the sacrum. This test consists of two parts: elongation test and shortening test.
- Ventral Sacrum Sliding: This technique can detect joint blockage and other symptoms that the patient may experience during the maneuver.
- Gillet test : hip flexion: with this maneuver a fixation on the ilium or a fixation on the sacral base is diagnosed.
Treatment
To treat joint problems in this area, different physical therapy techniques are used, such as:
- Postural care.
- Unlocking the joint.
- Slips.
- Stretching.
- Reorganization of neuromuscular chains.
In addition to those mentioned, other measures can also be used, such as application of ice, heat and rest, use of medication to combat pain, use of supports or corrections and controlled physical exercise.