Diagnosis Of Mandibular Tumors And Cysts
Mandibular tumors and cysts are tumors or lesions that form in the jaw or in the soft tissue of the mouth and face. A tumor is an abnormal growth or mass of tissue. A cyst is a lesion that contains liquid or semi-solid material.
In some cases, mandibular cysts and tumors are called odontogenic cysts, and they can vary greatly in size and severity. They are usually benign, but they can be aggressive and invade surrounding bones and tissue, as well as teeth.
Treatment options for mandibular tumors and cysts vary according to the type of growth and lesion, the stage of growth and the symptoms. Surgeons of the mouth, jaw, and face can treat the tumor or cyst by surgery, drug therapy, or a combination of both.
Types of tumors and mandibular cysts
There are many types of mandibular tumors and cysts; some of them are:
ameloblastoma
It is a relatively common tumor. It most often occurs in the mandible.
This tumor can reproduce after treatment. However, if a more aggressive surgical treatment is used, the possibility of recurrence is lower.
Giant cell central granuloma
Central granuloma is a benign lesion that is usually located in front of the mandible. Some of these tumors grow very fast and, in addition to causing pain, can destroy bones.
Central granulomas are characterized by their tendency to recur after surgical treatment.
dentigerous cyst
This cyst is originates from the tissue around the teeth before they emerge in the mouth
Odontogenic keratocyst
It is also known as keratocystic odontogenic tumor, due to its tendency to recur after surgical treatment. It is a benign cyst that grows slowly but can be destructive to local structures.
It usually develops in the lower jaw, close to the third molars. These cysts can also occur in people with an inherited condition called nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.
Odontogenic myxoma
Myxoma is another benign, slow-growing, rare tumor that usually develops in the lower jaw. It can be large and aggressively invade the jaw, surrounding tissue, and may even dislodge the teeth.
They are also susceptible to recurrence after surgical treatment.
odontoma
It is the most common odontogenic tumor. Odontomas usually do not trigger symptoms, but they can interfere with tooth development.
These types of tumors are made up of dental tissue that forms around a tooth in the jaw. They can look like teeth and can also be small or large calcified tumors.
Causes of mandibular tumors and cysts
Odontogenic cysts and maxillary tumors originate from cells and tissues involved in the normal development of teeth.
The cause of mandibular cysts and tumors is usually unknown. However, some of them are associated with genetic syndromes. People with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, also known as Gorlin syndrome, do not have a gene that suppresses tumors.
The genetic mutation that causes the syndrome is inherited and causes the development of multiple odontogenic keratocysts in the jaws, and different types of basal cell skin cancer.
Diagnosis of mandibular tumors and cysts
Most of the time, tumors and cysts cause no symptoms and discovery is accidental. However, in some cases, symptoms such as toothache, inflammation, local pain and bulging gums may appear.
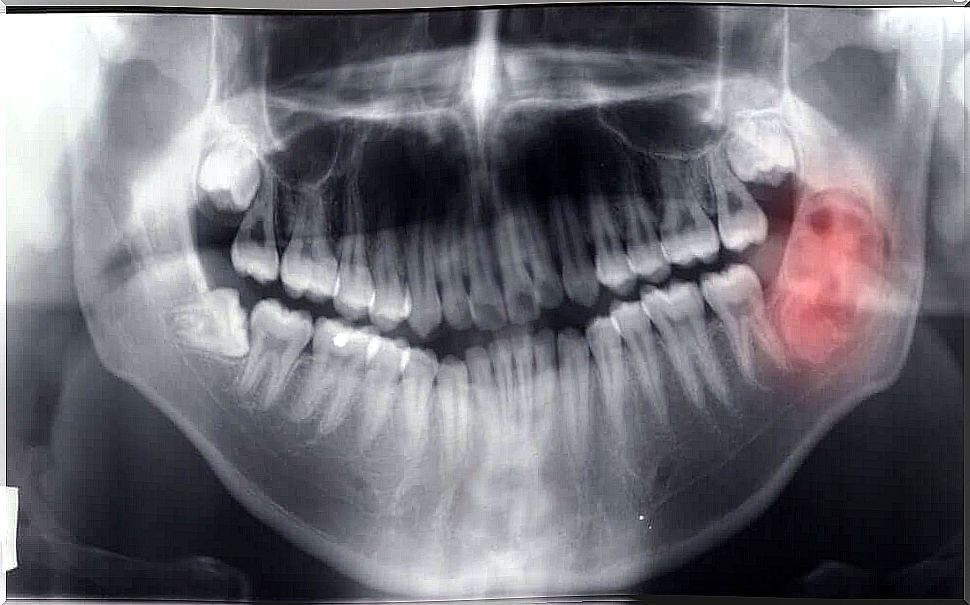
To obtain as much information about possible mandibular tumors and cysts, diagnostic tests such as radiographs, MRIs or orthopantomography will be requested.
In addition, a biopsy can be performed to remove a sample of cells from the tumor or cyst for analysis. With this information, the doctor will propose the appropriate treatment to treat the tumor or cyst as effectively as possible.